A road is a wide way leading from one place to another, especially one with a specially prepared surface which vehicles can use.
Roads consist of one or two roadways (British English: carriageways), each with one or more lanes and any associated sidewalks (British English: pavement) and road verges. A bike path (British English: cycle path) - a road for use by bicycles - may or may not run in parallel with other roads.
Other names for a road include: parkway; avenue; freeway, motorway or expressway; tollway; interstate; highway; thoroughfare; or primary, secondary, and tertiary local road.
Historically many roads were simply recognizable routes without any formal construction or maintenance.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defines a road as "a line of communication (travelled way) using a stabilized base other than rails or air strips open to public traffic, primarily for the use of road motor vehicles running on their own wheels", which includes "bridges, tunnels, supporting structures, junctions, crossings, interchanges, and toll roads, but not cycle paths".
The Eurostat, ITF and UNECE Glossary for Transport Statistics Illustrated defines a road as a "Line of communication (traveled way) open to public traffic, primarily for the use of road motor vehicles, using a stabilized base other than rails or air strips. [...] Included are paved roads and other roads with a stabilized base, e.g. gravel roads. Roads also cover streets, bridges, tunnels, supporting structures, junctions, crossings and interchanges. Toll roads are also included. Excluded are dedicated cycle lanes."
The 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Traffic defines a road as the entire surface of any way or street open to public traffic.
In urban areas roads may diverge through a city or village and be named as streets, serving a dual function as urban space easement and route. Modern roads are normally smoothed, paved, or otherwise prepared to allow easy travel.
Source: Wikipedia contributors. "Road." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, 19 Jun. 2021. Web. 28 Jun. 2021.
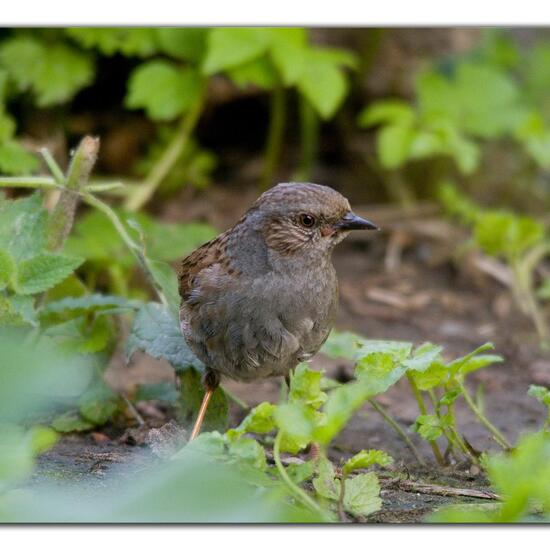


 A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Backyard on 08.06.2021. Dunnock (Prunella modularis) is a species of bird.
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Backyard on 08.06.2021. Dunnock (Prunella modularis) is a species of bird. 
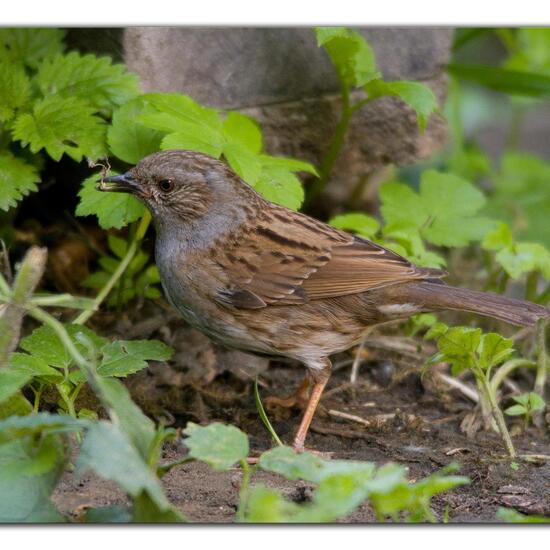 A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Backyard on 08.06.2021. Dunnock (Prunella modularis) is a species of bird.
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Backyard on 08.06.2021. Dunnock (Prunella modularis) is a species of bird. 
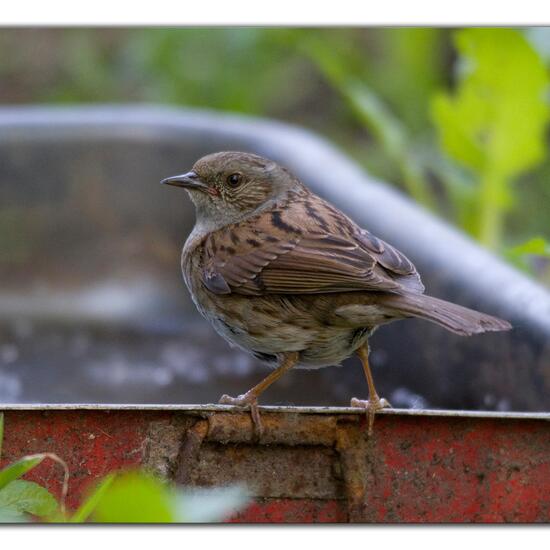
 A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 08.06.2021. Dunnock (Prunella modularis) is a species of bird.
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 08.06.2021. Dunnock (Prunella modularis) is a species of bird. 



