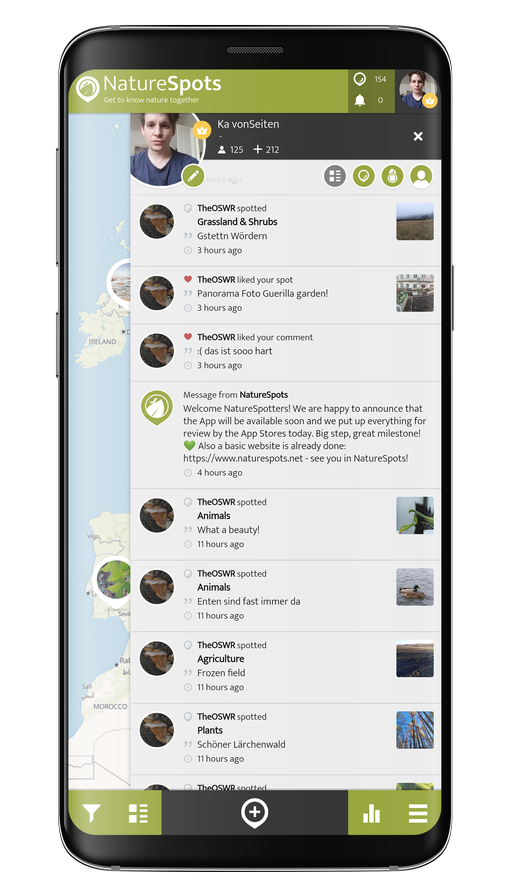
Hey, do you love Nature?
Observing and learning about nature is fun and can help to protect our environment. In the NatureSpots App, you can put up all kinds of nature sightings - from species to habitats. Join up and help to build a biodiversity data set and share your photos!
Create your account or download the NatureSpots App for your Smartphone now to join the community!
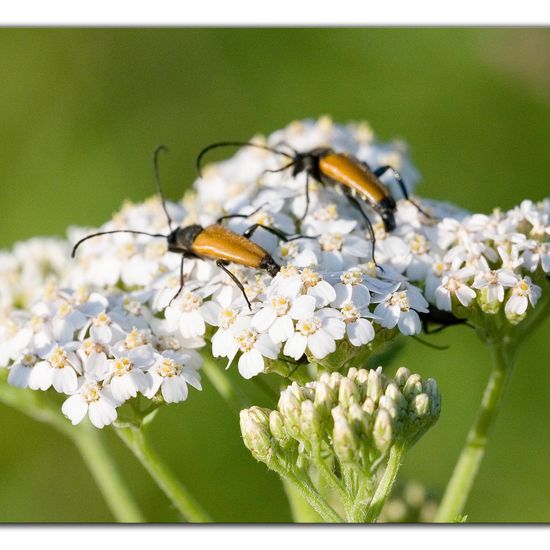
 A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Natural Meadow on 27.06.2022. Paracorymbia fulva (Paracorymbia fulva) is a .
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Natural Meadow on 27.06.2022. Paracorymbia fulva (Paracorymbia fulva) is a .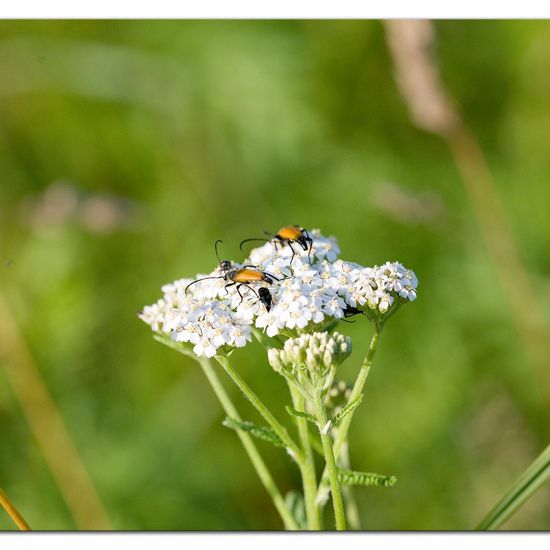  A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Natural Meadow on 27.06.2022. Paracorymbia fulva (Paracorymbia fulva) is a .
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Natural Meadow on 27.06.2022. Paracorymbia fulva (Paracorymbia fulva) is a .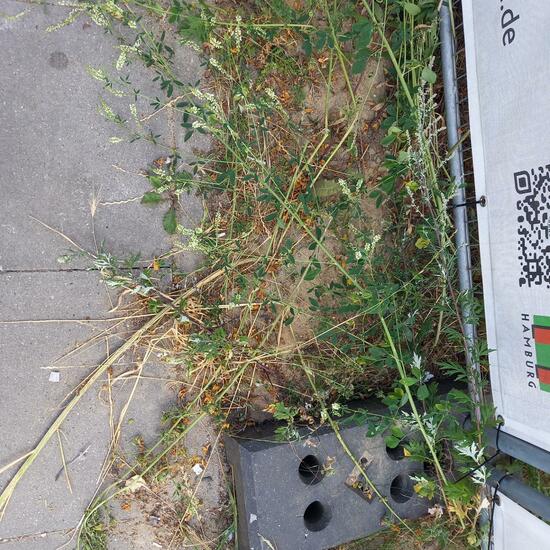  "Baustellen- Grün." says Mamabird in habitat Brownfield land on 30.06.2022. Melilotus albus (Melilotus albus) is a species of plant.
"Baustellen- Grün." says Mamabird in habitat Brownfield land on 30.06.2022. Melilotus albus (Melilotus albus) is a species of plant.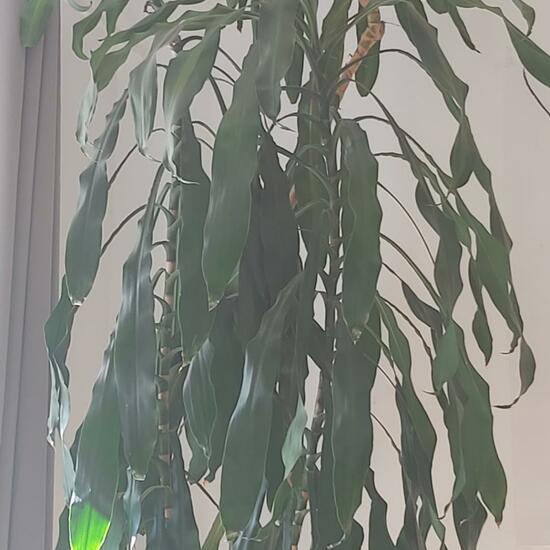  A discovery by Dominik Essl in habitat Living space or Indoor on 30.06.2022. of another species.
A discovery by Dominik Essl in habitat Living space or Indoor on 30.06.2022. of another species.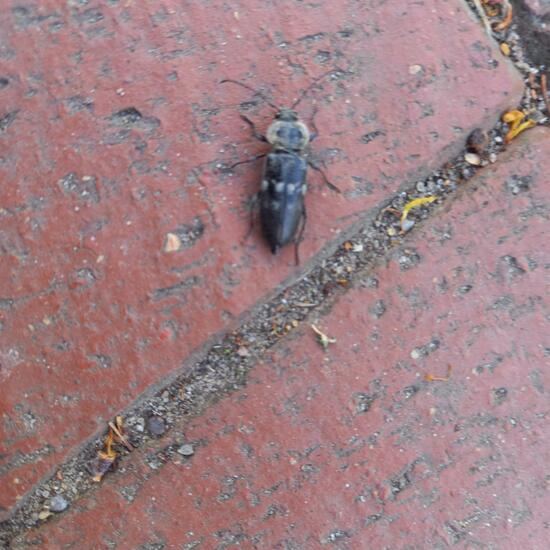  "Käfer. ?♀️" says Mamabird in nature on 30.06.2022. of another species.
"Käfer. ?♀️" says Mamabird in nature on 30.06.2022. of another species.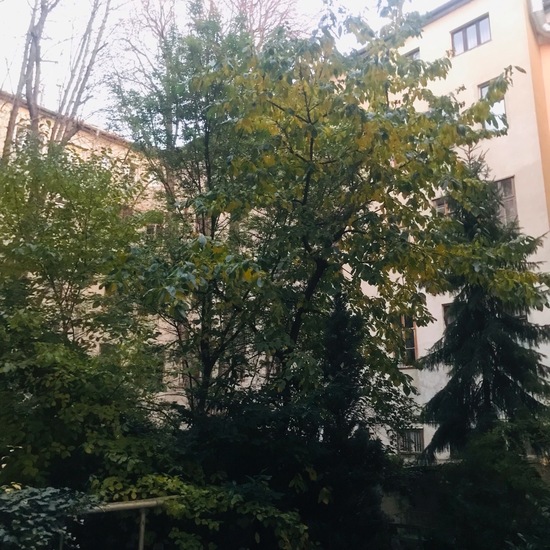  A discovery by Dominik Essl in habitat Backyard on 30.06.2022..
A discovery by Dominik Essl in habitat Backyard on 30.06.2022..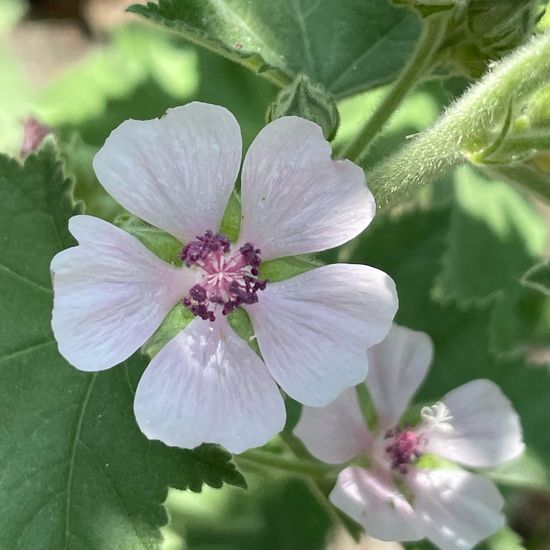  "Heute Blühbeginn beim Echten Eibisch (Althaea officinalis)" says Franz in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Althaea officinalis (Althaea officinalis) is a species of plant.
"Heute Blühbeginn beim Echten Eibisch (Althaea officinalis)" says Franz in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Althaea officinalis (Althaea officinalis) is a species of plant.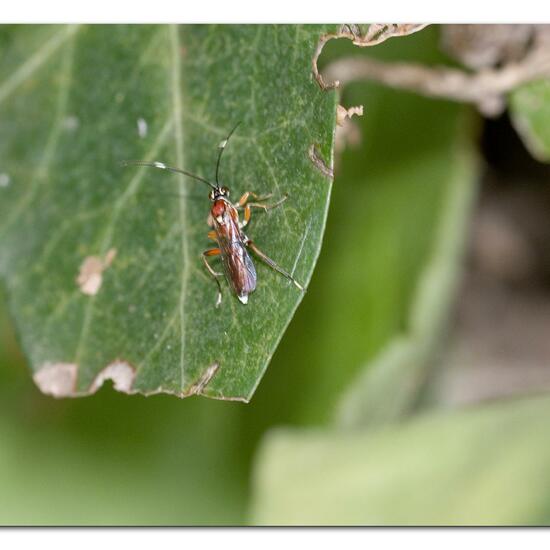  A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Crytea erythraea (Crytea erythraea) is a species of insect.
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Crytea erythraea (Crytea erythraea) is a species of insect.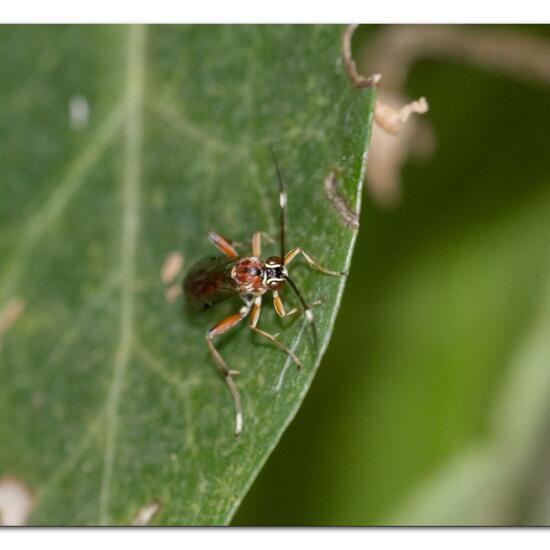  A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Crytea erythraea (Crytea erythraea) is a species of insect.
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Crytea erythraea (Crytea erythraea) is a species of insect.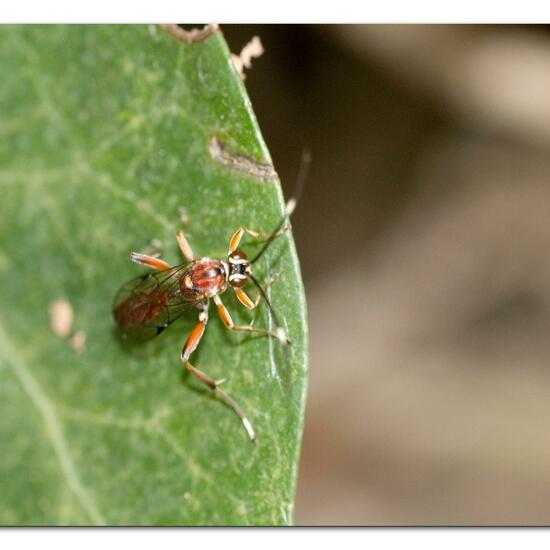  A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Crytea erythraea (Crytea erythraea) is a species of insect.
A discovery by Danny VG in habitat Garden on 30.06.2022. Crytea erythraea (Crytea erythraea) is a species of insect.